Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of molars that typically emerge in the late teens or early twenties. While they were once essential for our ancestors who had rough diets and experienced significant tooth wear, modern diets and dental practices have rendered these teeth less necessary. As a result, many people experience problems when their wisdom teeth begin to develop. This article will explore the various wisdom teeth symptoms, how they manifest, and what to expect if these teeth begin to make their appearance.
Does Everyone Have Wisdom Teeth?
A common question that arises when discussing wisdom teeth is whether everyone has them. The answer is no, not everyone develops wisdom teeth. In fact, some individuals may never experience the growth of these teeth at all, while others may have anywhere from one to four wisdom teeth. There are a few factors that influence the presence or absence of wisdom teeth:
- Genetics: Your family history plays a significant role in whether you develop wisdom teeth. If your parents or grandparents didn’t have them, it’s likely you won’t either.
- Evolution: Over time, human jaws have become smaller, and some evolutionary biologists believe that wisdom teeth are becoming less common due to changes in diet and oral health practices. This evolutionary trend might explain why some people simply never develop wisdom teeth.
- Jaw Size: Individuals with larger jaws may have more room for wisdom teeth, while those with smaller jaws might not have the space for these teeth to emerge, even if they do develop them.
In essence, while most people do develop wisdom teeth, not everyone does, and it’s not unusual for some to go through life without ever experiencing any symptoms related to them.
First Signs of Wisdom Teeth Coming In
The arrival of wisdom teeth can vary significantly from person to person. Some individuals may notice signs as early as their mid-teens, while others might not experience any symptoms until their early twenties. Knowing the early indicators of wisdom teeth growth can help you prepare for any potential complications. Common early signs include:
- Tenderness or Swelling in the Back of the Mouth: As wisdom teeth begin to push through the gums, you might experience swelling and tenderness at the very back of your mouth, near your molars.
- Jaw Stiffness or Pain: You might feel discomfort in the jaw, particularly when chewing or opening your mouth wide. This stiffness can be caused by the pressure the wisdom teeth exert on the surrounding teeth and jawbone.
- Gum Irritation: The gums around the wisdom teeth can become inflamed as the teeth start to emerge. You may notice redness or sensitivity when brushing the area.
- Headaches: As the teeth push through the gums, they can sometimes cause referred pain, leading to headaches or general discomfort in the head and neck region.
Early recognition of these signs is key to avoiding more serious complications later on. If you start noticing any of these wisdom teeth symptoms, it’s a good idea to schedule a visit with your dentist for an evaluation.

Wisdom Teeth Symptoms: What to Expect
The process of wisdom teeth coming in can vary, and so do the symptoms associated with their eruption. While some people might experience very mild symptoms, others might endure significant discomfort. Here’s a breakdown of common symptoms you might expect:
- Pain and Discomfort: One of the most common symptoms is pain in the back of the mouth. As the teeth push against the surrounding teeth and gums, they can cause moderate to severe discomfort. This pain may come and go or become more consistent as the teeth continue to grow.
- Swelling in the Gums or Jaw: As the wisdom teeth grow, the area around them may become swollen. This can cause noticeable puffiness in the gums or even the jaw, and the area might be tender to the touch.
- Difficulty Opening the Mouth: Due to the pressure exerted on the jaw, some individuals find it hard to fully open their mouths. This can make eating or speaking uncomfortable.
- Infection or Gum Disease: If the wisdom teeth only partially erupt, bacteria can become trapped under the gum flap, leading to an infection. Signs of infection include swelling, redness, pain, and pus. In severe cases, this can develop into a condition called pericoronitis.
- Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste: As bacteria accumulate around the partially erupted wisdom teeth, it can lead to persistent bad breath (halitosis) or an unpleasant taste in your mouth. This is often a sign of infection or decay.
- Shifting Teeth: As wisdom teeth push against the other molars, they can cause overcrowding, which may result in teeth shifting. This is particularly problematic for individuals who have previously undergone orthodontic treatment.
If these symptoms become severe or interfere with daily activities, it’s important to consult with a dentist or oral surgeon to discuss potential treatment options, such as extraction.
How Many Wisdom Teeth Do You Have?
Most people have four wisdom teeth—two on the top and two on the bottom. However, this number can vary. Here are some possible scenarios:
- Four Wisdom Teeth: This is the most common situation, with one wisdom tooth located in each corner of the mouth.
- Fewer Than Four Wisdom Teeth: Some individuals may have fewer than four wisdom teeth. For example, they might have one or two, or even none at all. In these cases, the missing teeth may have simply never developed.
- Supernumerary Wisdom Teeth (More Than Four): In rare cases, people may develop extra wisdom teeth, known as supernumerary teeth. This can complicate the situation, as more teeth mean less space in the mouth, increasing the likelihood of impaction and overcrowding.
Understanding how many wisdom teeth you have and monitoring their development is essential in managing any symptoms and preventing further dental issues.
Wisdom Teeth Extraction: A Common Solution
When wisdom teeth cause persistent problems, the most common treatment is extraction. Dentists or oral surgeons often recommend removal when the teeth are impacted (unable to fully emerge), causing pain, infection, or misalignment. Here’s what you can expect if you need your wisdom teeth removed:
- Pre-Extraction Consultation: Before removal, your dentist or surgeon will take X-rays to assess the position of the teeth and determine the best course of action.
- Surgery: The extraction itself is typically an outpatient procedure performed under local anesthesia, sedation, or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the removal and your comfort level.
- Post-Operative Care: After surgery, you’ll need to follow a recovery plan that includes rest, managing swelling and discomfort, and maintaining oral hygiene. Your dentist will provide guidelines on how to care for the extraction site to ensure proper healing.
- Recovery Time: Recovery from wisdom teeth extraction typically takes a few days to a week, depending on the individual. You may experience swelling, mild pain, and difficulty eating during the initial days, but with proper care, healing should progress smoothly.
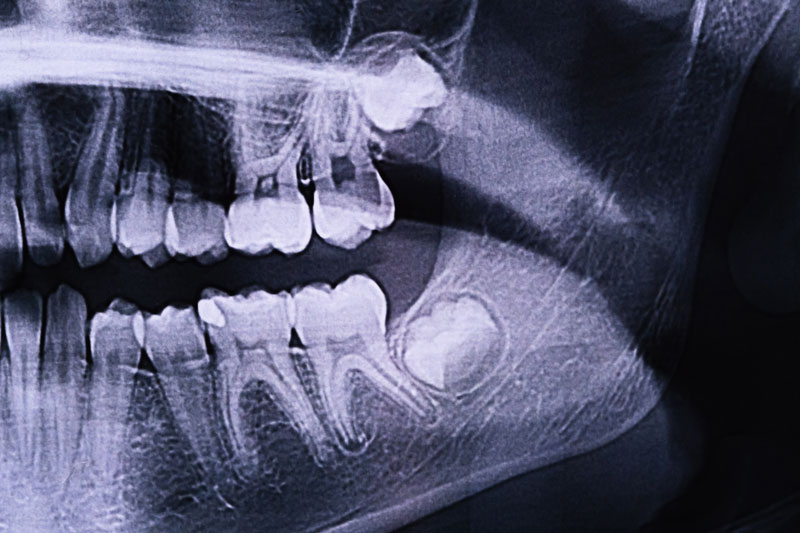
Managing Wisdom Teeth Symptoms
While wisdom teeth are a natural part of dental development for many people, the symptoms associated with their emergence can cause significant discomfort. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of wisdom teeth coming in—such as pain, swelling, and gum irritation—can help you take proactive steps to address potential complications.
If you experience any wisdom teeth symptoms that interfere with your daily life, consult with a dentist or oral surgeon. Early intervention can prevent more serious issues, such as infection or overcrowding, and ensure that your wisdom teeth are managed in a way that protects your overall dental health.
By staying aware of your wisdom teeth and how they are developing, you can take charge of your oral health and avoid complications that could affect the long-term health of your teeth and gums.